
Omega Centauri (NGC 5139) is the brightest and most spectacular globular cluster in the sky. NGC 5139 - Omega Centauri - Globular Cluster At 288 square degrees, it's the 55th largest constellation in the sky. For deep sky observers, Vulpecula contains the superb Dumbbell Nebula, a famous coathanger shaped open cluster and a few other open clusters. Locating the area of the sky where Vulpecula lies is easy it's wedged between Cygnus and Sagitta with the western half located roughly in the middle of the well observed Summer triangle (an asterism consisting of the bright stars Deneb, Vega and Altair). The only remains of the goose is the constellation's brightest star, Anser (α Vul).

It was then re-merged into a single entity - simply named Vulpecula - by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in the 20th century. Later the constellation was divided into two separate parts, Vulpecula and Anser. In his original illustration, Hevelius depicted an unfortunate goose carried in the jaws of a fox. The first means the little fox with the goose and the second the little fox and the goose.
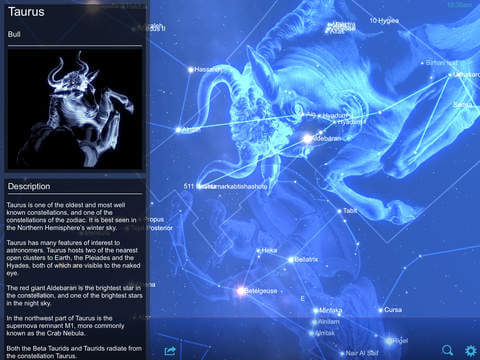
Originally it was known by two names, Vulpecula cum anser and Vulpecula et Anser. He included it in his influential 56 page star atlas, Firmamentum Sobiescianum, which was published posthumously in 1690. The constellation we know today was created by Johannes Hevelius. Strangely, it was not one of the original 48 constellations created by 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, even though the pattern of stars were clearly visible to him and other ancient Greeks and Romans. Vulpecula is a small, faint constellation located in the northern section of the sky. Along with marginally brighter Kornephoros (Beta Herculis) these are the only two stars in Hercules above magnitude +3.0.įor deep sky enthusiasts Hercules contains a sprinkle of globular clusters, challenging planetary nebulae and a host of faint galaxies. The brightest of the four, Zeta Herculis, shines at magnitude + 2.81 and is the second brightest star in the constellation. They are all between magnitudes 3 and 4 in brightness. The four stars of the Keystone are Eta Herculis, Zeta Herculis, Epsilon Herculis and Pi Herculis. The centrepiece of Hercules is a trapezoid shaped asterism commonly known as the Keystone. Although easily traceable under dark skies, the constellation can become elusive with just a hint of light pollution or when viewed under a moonlit sky. However, despite its large apparent size it's rather faint. Hercules is the 5th largest constellation and spans an impressive 1,225 square degrees of sky. The constellation of Hercules is one of the original 48 constellations plotted by 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy and remains today as one of the modern 88 constellations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
